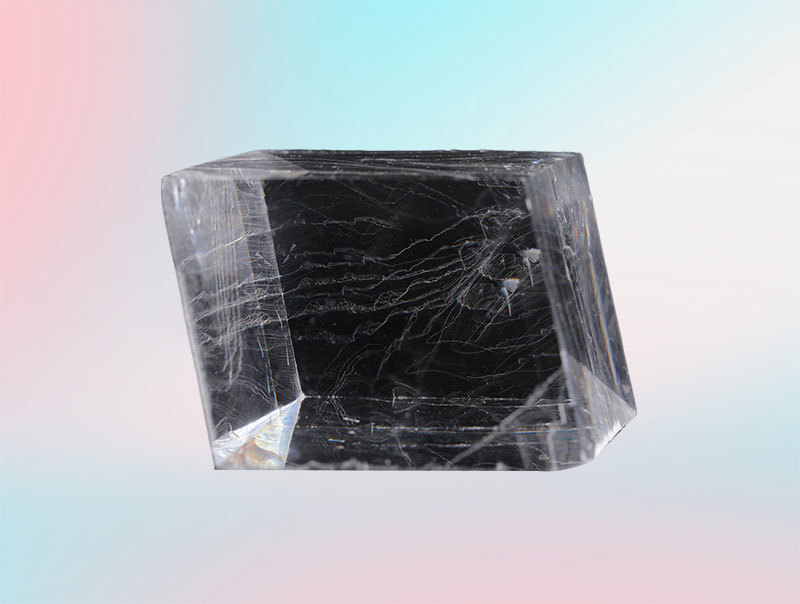
Understanding Crystal Polarizers: Essential Components in Optoelectronic Devices
Release Time:
2025-12-10
outline: Crystal polarizers are essential components in the field of optoelectronic devices, particularly due to their ability to manipulate light in sophisticated ways. This technology is integral to various applications ranging from displays to sensors and imaging systems. At its core, a crystal polarizer works by allowing only light waves vibrating in a particular direction to pass through while blocki
At its core, a crystal polarizer works by allowing only light waves vibrating in a particular direction to pass through while blocking others. This selective transmission of light is achieved through the unique properties of certain crystalline materials, which have a specific arrangement of atoms that affects the way light interacts with them. Commonly used materials for crystal polarizers include tourmaline and calcite, both of which exhibit birefringence—a phenomenon where a material has two different refractive indices based on the polarization direction of light.
The functioning of crystal polarizers is crucial in many optoelectronic devices. For instance, in liquid crystal displays (LCDs), polarizers are essential for controlling light to create visible images. They help enhance contrast and reduce reflections, thus improving overall display quality. In photography, crystal polarizers can be used in filters to reduce glare from reflective surfaces and to enhance color saturation.
Moreover, in scientific research, crystal polarizers are utilized in spectroscopic methods to study materials’ properties. By analyzing how a polarized light interacts with a sample, researchers can gain insights into molecular structures and dynamics.
One of the emerging trends in the use of crystal polarizers is their integration into augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) systems. As these technologies continue to evolve, the demand for high-quality optical components that can finely tune light will increase, making crystal polarizers even more significant.
When considering the implementation of crystal polarizers in your products, it is important to evaluate the specific requirements of your application. Factors such as wavelength range, thickness, and alignment tolerance can greatly influence the performance of the polarizer. Additionally, advancements in material science are leading to the development of new types of polarizers that can operate effectively across broader wavelengths and under various environmental conditions.
In summary, crystal polarizers play a pivotal role in the functionality of optoelectronic devices. Their ability to precisely control light opens up numerous possibilities in technology and scientific research. As innovations continue to unfold in this field, understanding the principles and applications of crystal polarizers will be key for professionals working in the industry.
The Advantages of Using Birefringent Crystals in Optical Engineering
outline: The Advantages of Using Birefringent Crystals in Optical Engineering Table of Contents 1. Introduction to Birefringent Crystals 2. Understanding Birefringence 3. Unique Properties of Birefringent Crystals 4. Applications of Birefringent Crystals in Optical Engineering 4.1 Wave Plates 4.2 Polarizers 4.3 Interferometer
2025-12-16
Understanding Polarizing Optics: Enhancing Visual Clarity in Electronics
outline: Polarizing optics is a fascinating field that deals with the behavior of light waves as they interact with materials that can filter and manipulate light. This technology is widely used in various electronic components, especially in optoelectronic devices. Understanding the principles of polarizing optics can significantly enhance the performance of these devices, leading to clearer images and mo
2025-12-14
The Fundamentals of Optical Prism Geometry and Its Practical Applications
outline: The Fundamentals of Optical Prism Geometry and Its Practical Applications Table of Contents 1. Introduction to Optical Prisms 2. Understanding Geometric Properties of Prisms 3. Types of Optical Prisms 4. Light Refraction in Prisms 5. Applications of Optical Prisms 5.1 Prisms in Optical Instruments 5.2 Prisms in Spectroscopy 5.3 Pris
2025-12-12